

学习资源
科普文章
构型Format的重要性:几何结构定义了双特异性抗体的功能(一) [1]
多特异性抗体可以以不同的形式format构建。双特异性抗体20多年的研发经验表明,format的设计和选择会对抗体功能产生重要影响。这对于引发细胞(间)的相互作用尤其如此,例如受体激活、受体内化、受体聚集或两个细胞之间免疫突触的形成。我们本次推荐的综述[1]涵盖影响多特异性抗体format功能性的设计参数,尤其关注引发 T 细胞募集的双特异性抗体。我们比较了分子量大小和域序列都相同、但几何形状不同的format。得出结论:某些format因其几何结构更有利于(人工)免疫突触【(artificial) immune synapses】的结构组成,从而效力更强。
1背景:不同应用,不同format
重组蛋白和抗体工程的技术创新衍生了许多不同的抗体format。根据文献,很难找到普适于所有应用场景的“万能”format。合适的抗体构型取决于所需的生物学效应及其潜在的结构条件。多特异性抗体可用于各种目的,包括 (1) 受体激活、(2) 受体阻断、(3) 受体内化、(4) 受体集聚、(5) 关联膜相关蛋白,或 (6) 细胞毒性效应细胞的重定向(图 1)。在这些应用场景中,有几个例子证明format会影响双特异性抗体 (bsAb) 的性能。
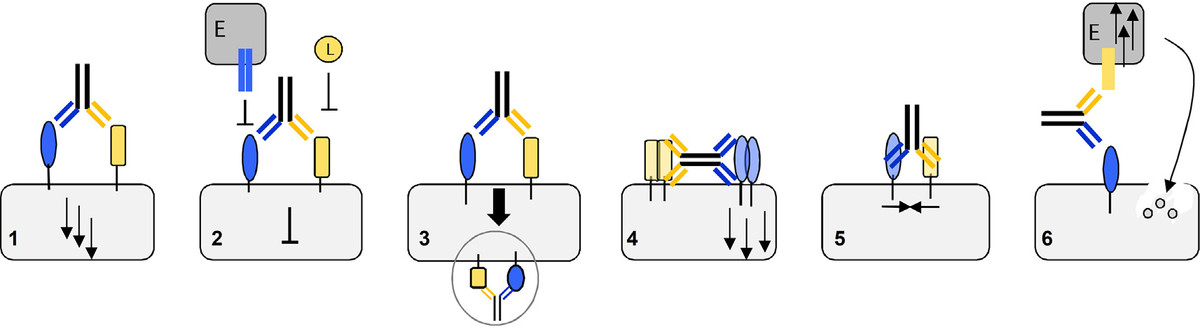
Fig. 1. Application areas of bispecific antibodies: 1) Receptor activation. 2) Receptor blocking and inhibition of soluble ligand (L) or membrane-bound ligand binding, e.g. of effector cells (E). 3) Receptor internalization. 4) Receptor clustering. 5) Receptor association. 6) Bicellular binding and retargeting of effector cells (E).
图1. 双特异性抗体的应用场景:1)受体激活;2) 受体阻断,抑制其与配体的结合,配体可能是可溶性的或者在效应细胞 (E)膜表达上的;3) 受体内化;4) 受体集聚;5) 受体结合;6) 效应细胞 (E) 的重定向,与目标细胞的结合。
受体激活
受体激活 (1) 和诱导下游信号以实现特定生物学功能是激动性抗体的设计思路。Shi等人设计了类 IgG 、四价、双互补位的format,其在每个 N 末端包含单链 VH 结合剂。互补位的近距离模拟天然配体,从而激活内分泌成纤维细胞生长因子 (FGF) 21 受体 (FGFR)。他们仔细选择了独特的抗体几何结构,并证明其对于诱导激动作用至关重要(图2)[2] 。其他人最近发表了同样的format,他们也通过靶向 CD40、OX40和/或4-1BB [34]来检测激动[3]。
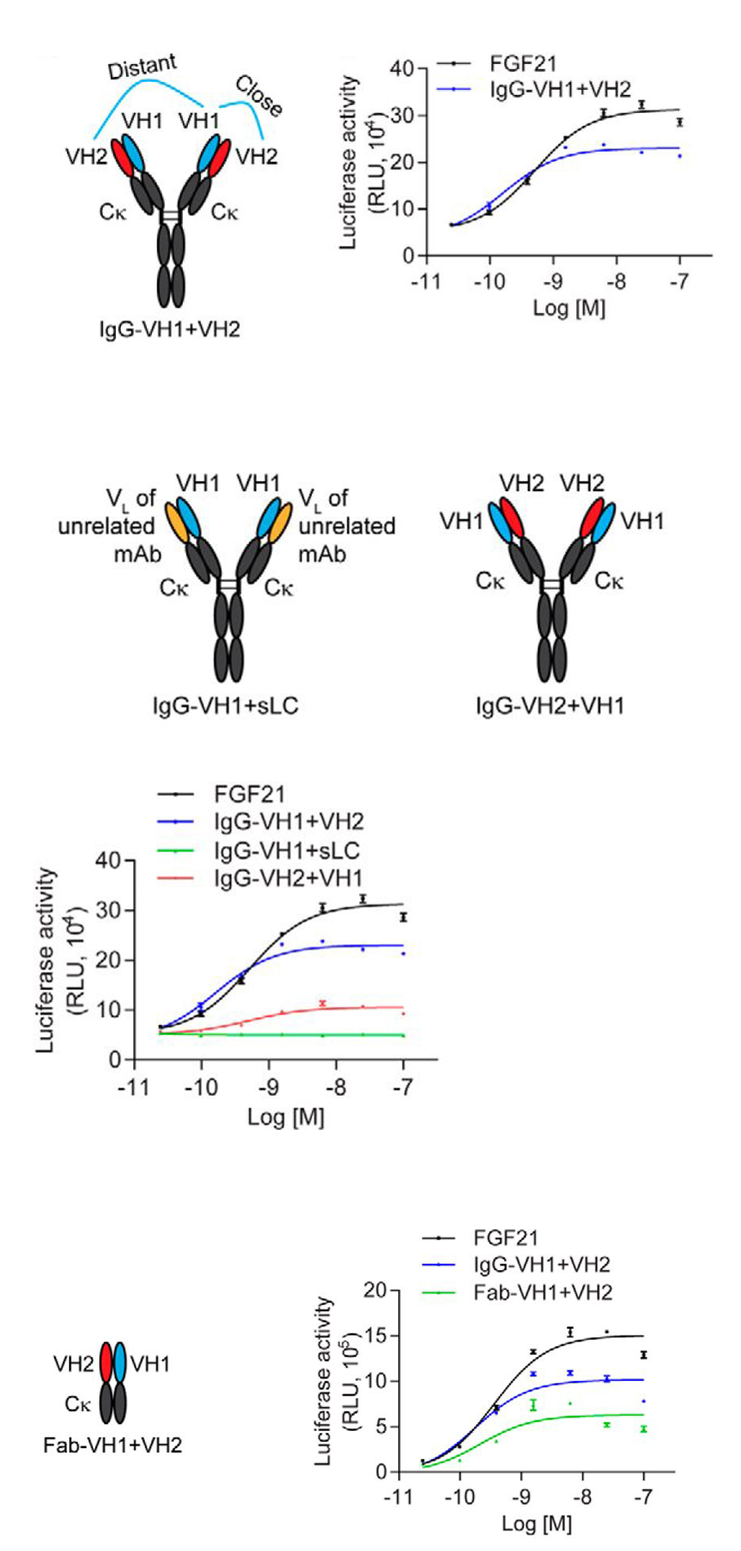
Figure 2.The correct orientation of VH1 and VH2 domains is required for optimal agonistic activity. VH1, VH2, and FGF21 bind to distinct regions on β-Klotho. In FGF21-responsive CHO reporter cells expressing human β-Klotho and FGFR1c, IgG-VH1+VH2 activated receptor signaling with potency similar to that of FGF21 (EC50 = 0.5 nm). When the positions of VH1 and VH2 are swapped, by placing VH2 on the heavy chain and VH1 on the light chain (IgG-VH2+VH1), the agonistic activity of this molecule was significantly attenuated, achieving only one third of the maximal response of IgG-VH1+VH2.
图2 VH1和VH2结构域的正确取向是最佳激动活性所必需的。VH1、VH2和FGF21与β-Klotho上的不同区域结合。在表达人β-Klotho和FGFR1c的FGF21应答CHO报告细胞中,IgG-VH1+VH2激活受体信号,其效力与FGF21相似(EC50=0.5 nm)。当VH1和VH2的位置互换时,通过将VH2放在重链上而将VH1放在轻链上(IgG-VH2+VH1),该分子的激动活性显著减弱,仅达到IgG-VH1+VH2最大反应的三分之一。
Milutinovic等人合成了一种二价 Y 形 Surrobody,它可以刺激死亡受体 DR4 和 DR5。该分子显示出比单特异性 DR4 和 DR5 抗体组合更强的效力,表明其独特的介导激动作用的特性(图3)[4]。
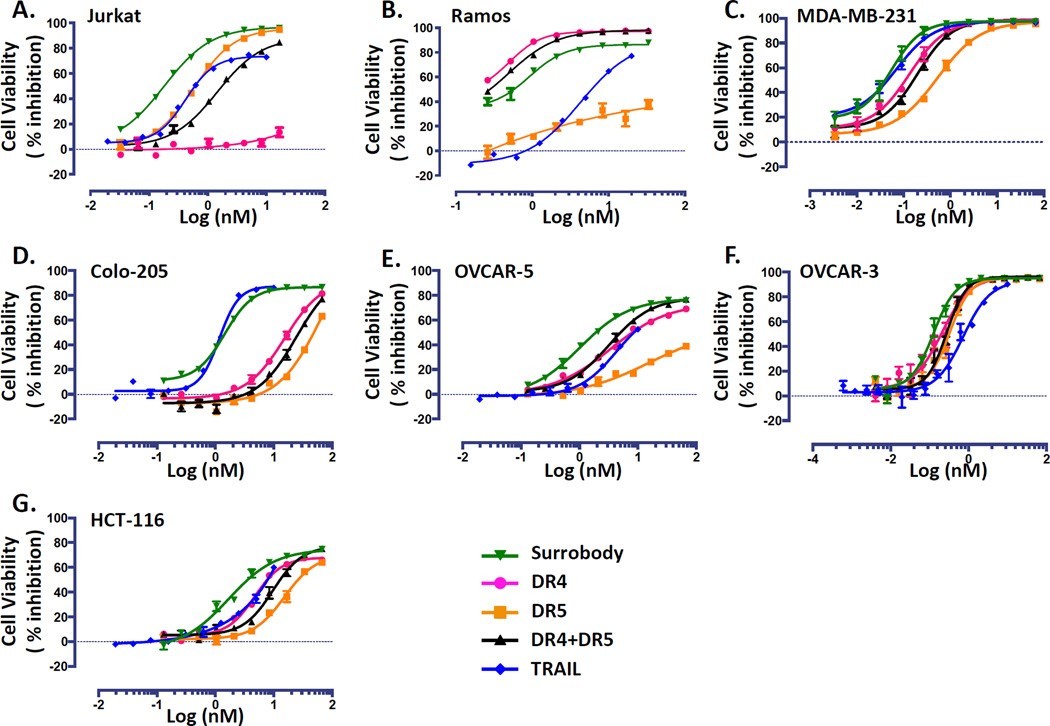
Figure 3. Death receptor dual agonist Surrobody is a more potent inducer of tumor cell death than DR4 or DR5 monospecific antibodies. Various TRAIL-sensitive cancer cell lines were plated at a density of 750 cells/well in 384 wells. The next day cells were cultured with increasing concentrations of monospecific DR4 antibody (pink), monospecific anti-DR5 antibody (orange), the combination of anti-DR4 and anti-DR5 antibodies (black), death receptor dual agonist Surrobody (green), or TRAIL (blue) for 48 hr. Before addition to cells, all the antibodies and Surrobody were incubated for 5 minutes with 0.5× molar ratio of protein G to facilitate clustering. Relative cell viability was estimated from cellular ATP measurements using the Cell Titer Glo reagent (Promega), expressing data as % inhibition of cell survival (mean ± SEM; n= 4). Data are shown for Jurkat (A), Ramos (B), MDA-MB-231 (C), Colo-205 (D), Ovcar-3 (E) and Ovcar-5 (F) and HCT116 (G) cell lines.
图3 死亡受体双激动剂Surrobody是比DR4或DR5单特异性抗体更有效的肿瘤细胞死亡诱导剂。在384个孔中,以750个细胞/孔的密度对各种TRAIL敏感的癌症细胞系进行电镀。第二天,将细胞与浓度增加的单特异性DR4抗体(粉色)、单特异性抗DR5抗体(橙色)、抗DR4和抗-DR5抗体的组合(黑色)、死亡受体双激动剂Surrobody(绿色)或TRAIL(蓝色)一起培养48小时,将所有抗体和Surrobody与0.5×。使用cell Titer Glo试剂(Promega)从细胞ATP测量中估计相对细胞活力,将数据表示为细胞存活抑制%(平均值±SEM;n=4)。显示了Jurkat(A)、Ramos(B)、MDA-MB-231(C)、Colo-205(D)、Ovcar-3(E)和Ovcar-5(F)和HCT116(G)细胞系的数据。
就在最近,Genentech 公司研究人员展示巨噬细胞上 MerTK(Mer 酪氨酸激酶)受体通路的激活,可以导致 CD20 阳性 B 细胞的吞噬作用。他们使用简单的 1 + 1 IgG format (图4) [5]。
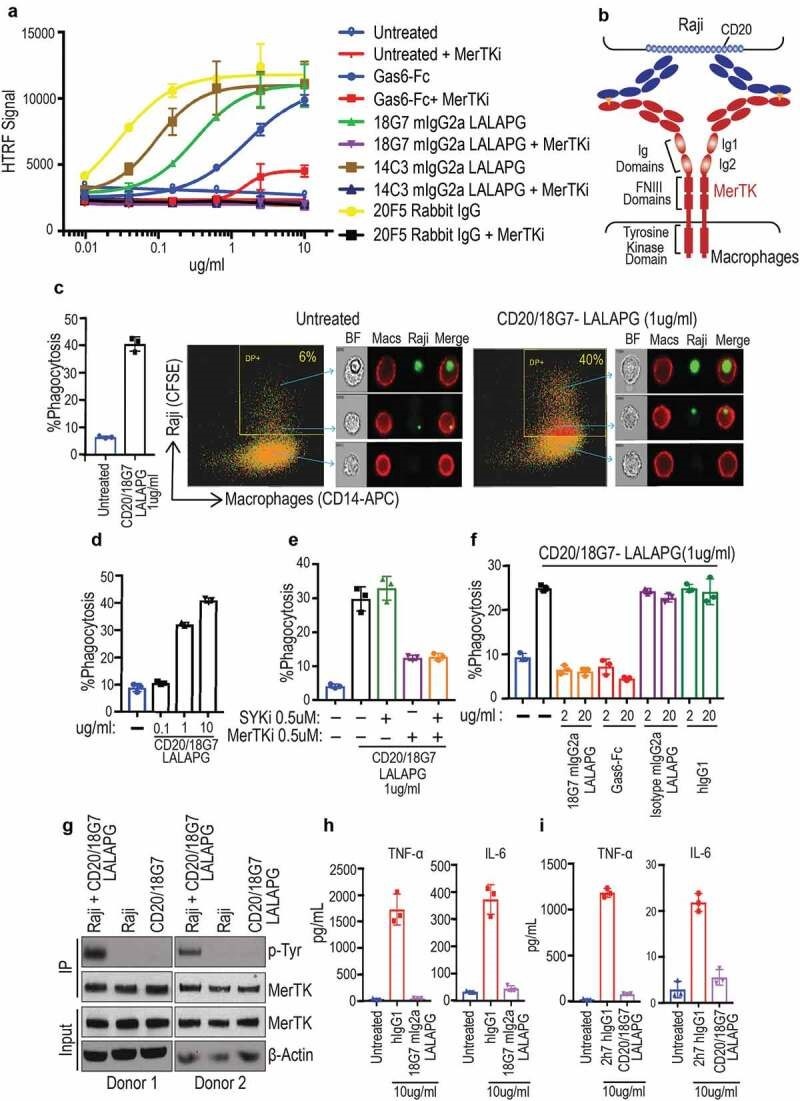
Figure 4. Identifying and characterizing MerTK agonist antibodies for engineering anti-CD20/MerTK bispecific antibodies capable of inducing phagocytosis of B cells by macrophages (a) Characterization of lead MerTK agonist antibodies measured by their ability to induce pAKT (Ser-473) in human MerTK+ macrophages using HTRF assay (Mean ± S.D of 2 technical replicates). Gas6-Fc is a positive control for MerTK activation. (b) Schematic depiction of B cell-dependent engagement of MerTK via anti-CD20/MerTK bispecific antibody. (c) Imagestream analysis of phagocytosis of live Raji cells by human primary macrophages in the presence of indicated bispecific antibody. A representation of Imagestream analysis is shown. Quantification is also presented (Mean ± S.D of one replicate each from 3 donors). (d-f) Flow cytometric analysis of phagocytosis of live Raji cells by human primary macrophages in the presence of indicated bispecific antibody, inhibitors and blocking agents (Mean ± S.D of one replicate each from 3 donors) (g) Activation of MerTK (phosphotyrosine) by the bispecific antibody in the presence of target Raji cells. Results are from using macrophages derived from two different human donors. See Supplementary Figure 5 for extended western blot. (h-i) TNF and IL-6 production by human primary macrophages stimulated with indicated plate coated antibodies. (Mean ± S.D of one replicate each from three different donors).
图4鉴定和表征能够诱导巨噬细胞吞噬B细胞的工程化抗CD20/MerTK双特异性抗体的MerTK激动剂抗体(a)使用HTRF测定法(2个技术重复的平均值±S.D),通过其在人MerTK+巨噬细胞中诱导pAKT(Ser-473)的能力来测定MerTK激动抗体的特性。Gas6-Fc是MerTK激活的阳性对照。(b) MerTK通过抗CD20/MerTK双特异性抗体的b细胞依赖性结合的示意图。(c) 在指示的双特异性抗体存在下,人原代巨噬细胞吞噬活Raji细胞的图像流分析。显示了Imagestream分析的表示。还提供了定量(来自3个供体的每个重复的平均值±S.D)。(d-f)在指示的双特异性抗体、抑制剂和阻断剂存在的情况下,人原代巨噬细胞对活Raji细胞的吞噬作用的流式细胞术分析(平均值±S.d,来自3个供体的每个重复一次)(g)在靶Raji细胞存在时,双特异性的抗体激活MerTK(磷酸酪氨酸)。结果来自两种不同的人类供体的巨噬细胞。关于扩展的蛋白质印迹,参见补充图5。(h-i)用指示的平板包被抗体刺激的人原代巨噬细胞产生的TNF和IL-6。(三个不同供体各重复一次的平均值±S.D)。
受体阻断
受体阻断 (2) 目前在癌症免疫治疗方法中占有重要地位。针对抑制性免疫检查点的双特异性拮抗分子在克服肿瘤逃避机制方面显示出预期的结果。一个突出的例子是 LAG-3 和 PD-1 等免疫检查点的双重封锁,可诱导抗肿瘤免疫[6, 7]。正在进行的具有多种双特异性抗体形式的临床试验数量惊人。然而,激动性抗体的产生具有挑战性(它们取决于亲和力和内在功效),而设计阻断抗体主要依赖于寻找与天然配体竞争的高亲和力结合剂,因此被认为不那么复杂。
抗体诱导的受体内化
抗体诱导的受体内化 (3) 在抗体药物偶联物 (ADC) 重定向中起着重要作用。可以证明,与单价形式相比,EGFR 的二价结合以及由此触发的二聚化导致受体-抗体复合物的内化显着更高[8, 9]。Niewoehner 等人分析了不同的format以实现血脑屏障转胞吞作用。转铁蛋白受体 (TfR) 的单价靶向导致比体内二价 形式高 55 倍的脑暴露。据推测,二价 TfR 结合导致大量受体二聚化,并随后路由至溶酶体途径。另一方面,单价结合可以允许生理结合伴侣转铁蛋白同时复合,并将两种分子共同转运到近腔侧,而抗体不会发生溶酶体降解[10, 11] 。
受体超聚类
受体超聚类 (4) 是激活肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族 (TNFRSF) 的受体所必需的,例如激活细胞凋亡途径的死亡受体 (DR)。诱导信号级联的激动性抗体的产生具有挑战性,并且在早期方法中临床疗效有限。Yang等人用四价双互补位抗体实现了强大的内在激动作用,而二价双互补位控制分子没有触发任何激活(图5)[12]。
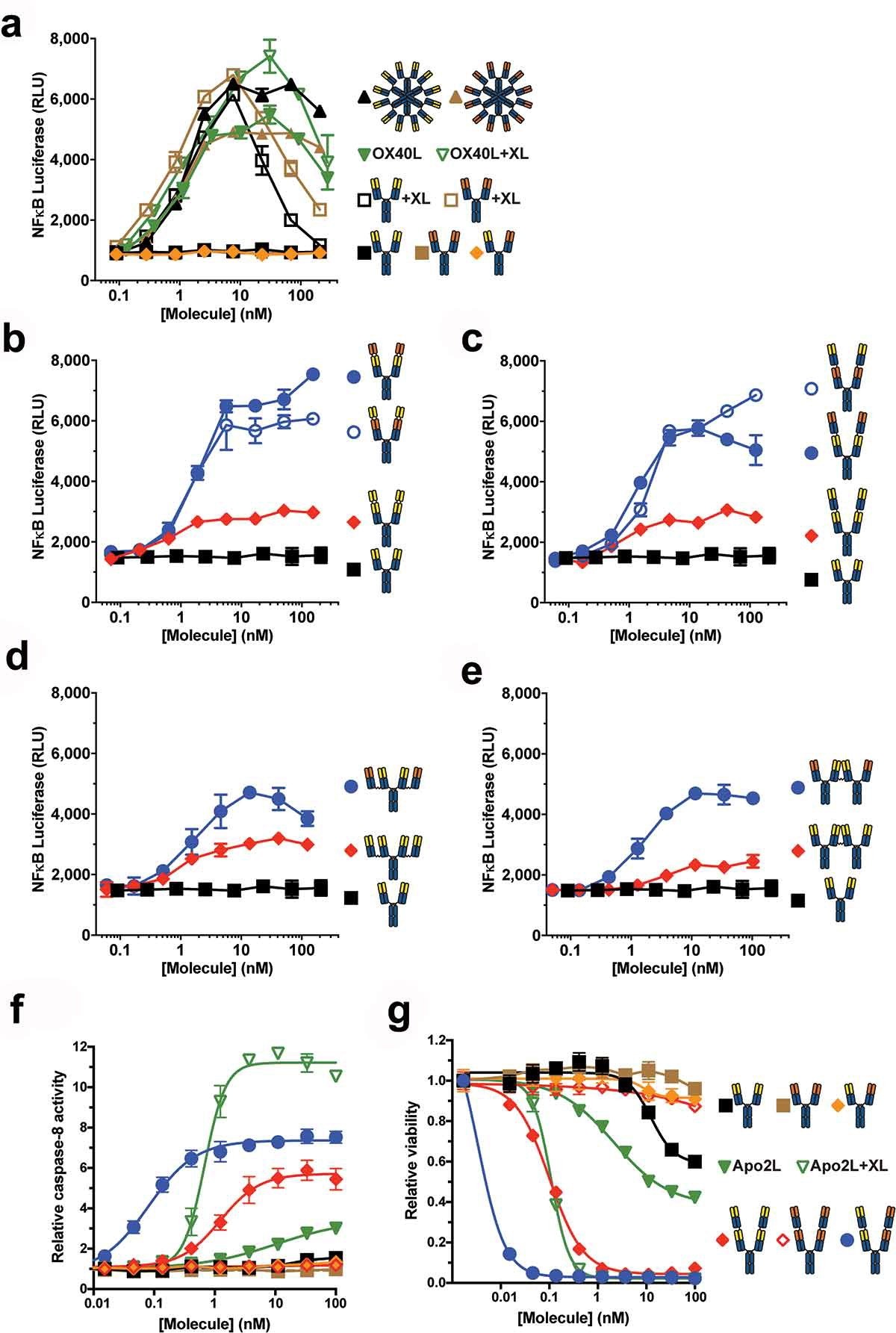
Figure 5. Tetravalent biepitopic antibody formats enable intrinsic agonism of TNFRSFs. (a) NF-κB signaling mediated by OX40L-huIgG1 Fc fusion (OX40L) and anti-OX40 antibody formats. IgG1 (squares) and OX40L (downward triangles) were tested with (+XL) and without extrinsic secondary crosslinking. Orange triangle represents a bivalent biepitopic antibody (Ab1/Ab2), and upward triangles represent hexameric variant antibodies (RGY). (b–e) OX40 NF-κB signaling activity mediated by tetravalent biepitopic (blue) and monoepitopic (red) antibody formats: r:Fv-IgG (b), r:Fab-IgG (c), c:Fab-IgG (d) or c:IgG-IgG (e). (f) DR5 driven caspase-8 activity and (g) anti-proliferative activity in COLO 205 cells mediated by multivalent and multiepitopic antibody formats and soluble Flag-Apo2L. For all tetravalent formats (b–g) blue circles indicate biepitopic formats and red diamonds indicate monoepitopic formats, respectively. The x-axis for each graph represents the molar concentration of each complete molecule irrespective of number of receptor binding units; i.e., 1 nM of a bivalent antibody has two binding sites, whereas a 1 nM equivalent of an r:Fv-IgG has four binding sites.
图5 四价双表位识别的抗体形式能够实现TNFRSF的内在激动作用。(a) 由OX40L-huIgG1-Fc融合(OX40L)和抗OX40抗体形式介导的NF-κB信号传导。IgG1(正方形)和OX40L(向下三角形)用(+XL)和无外部二次交联进行测试。橙色三角形表示二价双皮体抗体(Ab1/Ab2),向上三角形表示六聚体变体抗体(RGY)。(b–e)由四价双表位(蓝色)和单表位(红色)抗体形式介导的OX40 NF-κ。(f) DR5驱动的caspase-8活性和(g)由多价和多表位抗体格式和可溶性Flag-Apo2L介导的COLO 205细胞中的抗增殖活性。对于所有四价格式(b–g),蓝色圆圈表示双表位格式,红色菱形表示单表位格式。每个图的x轴表示每个完整分子的摩尔浓度,而与受体结合单元的数量无关;即,1nM的二价抗体具有两个结合位点,而1nM当量的r:Fv IgG具有四个结合位点。
布鲁克等人设计了一种针对肿瘤抗原 FAP(成纤维细胞激活蛋白)和 DR5 的 2 + 2 格式。他们可以表明,两种抗原以顺式方向的二价结合导致亲和力驱动的 DR5 超聚簇,随后强烈诱导细胞凋亡。与依赖 FcγR 相互作用的其他聚簇方法相比,他们利用肿瘤间质中的 FAP 表达以靶向方式促进 DR5 的超聚簇(图6和图7)[13]。

Figure 6. FAP-DR5 BsAb and apoptosis activity. A, principle of tumor-targeted apoptosis by BsAbs consisting of a CrossFab anti-FAP unit (mAb007 or mAb082) fused to the C-terminus of the drozitumab heavy chain using a 20mer GS linker. The mAb007 anti-FAP moiety was fused to drozitumab heavy chain in either a VHCL or VLCH1 configuration.
图6 FAP-DR5-BsAb和凋亡活性。A、 BsAb的肿瘤靶向凋亡原理,该BsAb由使用20mer GS接头融合到卓齐单抗重链C末端的CrossFab抗FAP单元(mAb007或mAb082)组成。mAb007抗FAP部分以VHCL或VLCH1构型与卓齐单抗重链融合。
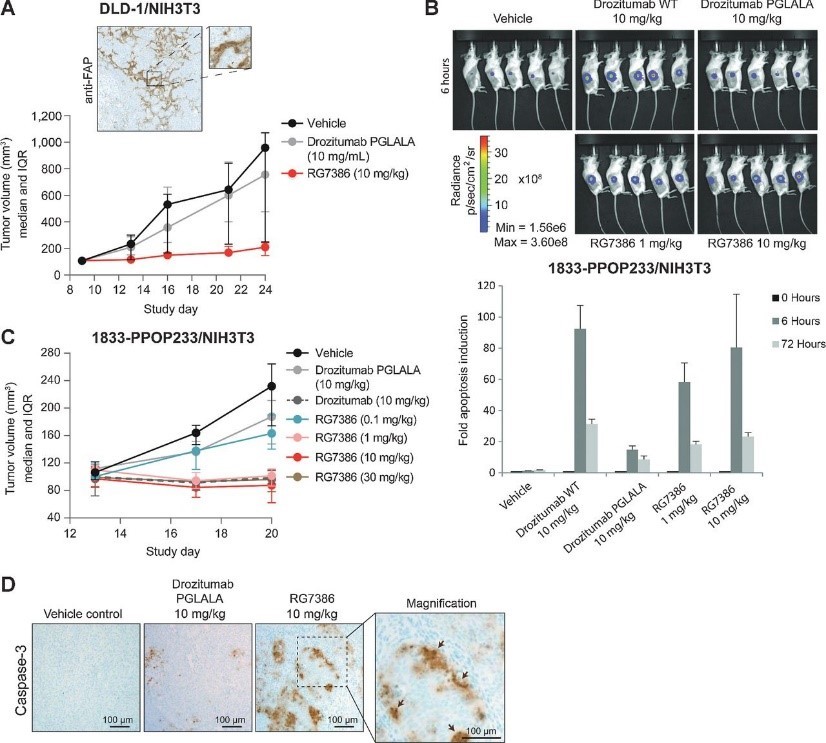
Figure 7. RG7386 induces tumor cell apoptosis in vivo in human xenograft mouse models. A, antitumor efficacy of RG7386 in a mouse xenograft model. Nude mice were subcutaneously coinjected with human DLD-1 and NIH3T3 cells and subjected to RG7386 (twice weekly doses) or Drozitumab_PGLALA antibody treatment when tumor volume was approximately 100 mm3 in size. Shown is a representative FAP IHC of the tumor (median tumor volume and interquartile range (IQR); n = 10 animals/group). B and C, apoptosis was monitored in mice coinjected with bone-metastasizing MDA-MB-231 1833-PPOP233 tumor cells and NIH3T3 cells. B, in vivo analysis of apoptosis using a luminescence caspase 3/7 activation reporter assay in response to the indicated treatments over 72 hours. Luminescence images were taken at 0, 6, and 72 hours posttreatment. Representative luminescence images at 6 hours are shown (mean ± SEM; n = 5 animals/group). C, analysis of TGI in the same model in response to RG7386 (median tumor volume and IQR; n = 10 animals/group). D, IHC validation of caspase-3 activation in response to RG7386.
图7. RG7386在人异种移植小鼠模型中诱导体内肿瘤细胞凋亡。A、 RG7386在小鼠异种移植模型中的抗肿瘤作用。将裸小鼠与人DLD-1和NIH3T3细胞皮下共注射,并在肿瘤体积约为100mm3时接受RG7386(每周两次剂量)或Drozumab_PGLALA抗体治疗。所示为肿瘤的代表性FAP IHC(肿瘤体积中值和四分位间距(IQR);n=10只动物/组)。在与骨转移MDA-MB-231 1833-PPOP233肿瘤细胞和NIH3T3细胞共同注射的小鼠中监测细胞凋亡。B、 使用发光caspase3/7活化报告物测定法在体内分析细胞凋亡,以响应72小时以上的指示处理。在治疗后0、6和72小时拍摄发光图像。显示了6小时时的代表性发光图像(平均值±SEM;n=5只动物/组)。C、 分析同一模型中对RG7386的TGI反应(肿瘤体积中值和IQR;n=10只动物/组)。D、 响应RG7386的caspase-3激活的IHC验证。
另一个应用领域是抗体介导的两种或多种蛋白质在磷脂膜上的结合[14]。血友病 A 是一种遗传性出血性疾病,由凝血蛋白因子 VIII 缺失引起。在生理条件下,FVIII 作为辅助因子促进酶-底物复合物 FIXa-FX 的结合,从而导致 FX 的激活,这反过来又是凝血级联反应中的关键因素[15]。Chugai公司的研究人员生成了一种类IgG结构的bsAb,其几何形状明确,可模仿 FVIII 的结构和变构特性,从而恢复级联[16]。该分子称为 Hemlibra® (emicizumab),是两种已获批准的 bsAb 之一[17][29]。
关于本篇综述关于TCE以及其Format对于免疫突触形成及抗体功能的影响会在后续微信文章中介绍,敬请读者关注。
本文仅作信息分享,不代表礼进生物公司立场和观点,也不作治疗方案推荐和介绍。如有需求,请咨询和联系正规医疗机构。
参考文献1.Dickopf, S., G.J. Georges, and U. Brinkmann, Format and geometries matter: Structure-based design defines the functionality of bispecific antibodies. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2020. 18: p. 1221-1227.
2.Shi, S.Y., et al., A biparatopic agonistic antibody that mimics fibroblast growth factor 21 ligand activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2018. 293(16): p. 5909-5919.
3.Ljungars, A., et al., A bispecific IgG format containing four independent antigen binding sites. Sci Rep, 2020. 10(1): p. 1546.
4.Milutinovic, S., et al., Dual Agonist Surrobody Simultaneously Activates Death Receptors DR4 and DR5 to Induce Cancer Cell Death. Mol Cancer Ther, 2016. 15(1): p. 114-24.
5.Kedage, V., et al., Harnessing MerTK agonism for targeted therapeutics. MAbs, 2020. 12(1): p. 1685832.
6.Woo, S.R., et al., Immune inhibitory molecules LAG-3 and PD-1 synergistically regulate T-cell function to promote tumoral immune escape. Cancer Res, 2012. 72(4): p. 917-27.
7.LaMotte-Mohs, R., et al., Abstract 3217: MGD013, a bispecific PD-1 x LAG-3 Dual-Affinity Re-Targeting (DART®) protein with T-cell immunomodulatory activity for cancer treatment. Cancer Research, 2016. 76(14_Supplement): p. 3217-3217.
8.Jin, J., et al., An anti-EGFR × cotinine bispecific antibody complexed with cotinine-conjugated duocarmycin inhibits growth of EGFR-positive cancer cells with KRAS mutations. Exp Mol Med, 2018. 50(5): p. 1-14.
9.Fan, Z., et al., Antibody-induced epidermal growth factor receptor dimerization mediates inhibition of autocrine proliferation of A431 squamous carcinoma cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1994. 269(44): p. 27595-27602.
10.Niewoehner, J., et al., Increased Brain Penetration and Potency of a Therapeutic Antibody Using a Monovalent Molecular Shuttle. Neuron, 2014. 81(1): p. 49-60.
11.Weber, F., et al., Brain Shuttle Antibody for Alzheimer’s Disease with Attenuated Peripheral Effector Function due to an Inverted Binding Mode. Cell Reports, 2018. 22(1): p. 149-162.
12.Yang, Y., et al., Tetravalent biepitopic targeting enables intrinsic antibody agonism of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily members. mAbs, 2019. 11(6): p. 996-1011.
13.Brünker, P., et al., RG7386, a Novel Tetravalent FAP-DR5 Antibody, Effectively Triggers FAP-Dependent, Avidity-Driven DR5 Hyperclustering and Tumor Cell Apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther, 2016. 15(5): p. 946-57.
14.Bargou, R., et al., Tumor Regression in Cancer Patients by Very Low Doses of a T Cell–Engaging Antibody. Science, 2008. 321(5891): p. 974-977.
15.Lenting, P.J., C.V. Denis, and O.D. Christophe, Emicizumab, a bispecific antibody recognizing coagulation factors IX and X: how does it actually compare to factor VIII? Blood, 2017. 130(23): p. 2463-2468.
16.Kitazawa, T., et al., A bispecific antibody to factors IXa and X restores factor VIII hemostatic activity in a hemophilia A model. Nat Med, 2012. 18(10): p. 1570-4.
17.Labrijn, A.F., et al., Bispecific antibodies: a mechanistic review of the pipeline. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2019. 18(8): p. 585-608.








 沪公网安备 31011502015333号
沪公网安备 31011502015333号